Search results
Search for "polymer nanoparticles" in Full Text gives 3 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Host–guest interactions in nor-seco-cucurbit[10]uril: novel guest-dependent molecular recognition and stereoisomerism
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1705–1711, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.166
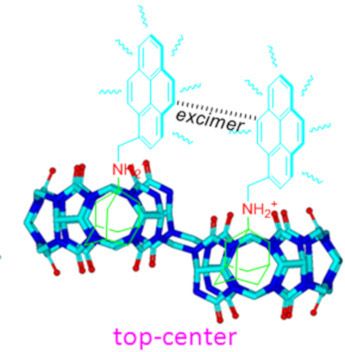
- adamantaneammonium (ADA) or alkylammonium ions into the cavity, forming a ternary complex. The novel binding capacity of NS-CB[10] has been utilized to form supramolecular polymers [24][25][26] and polymer nanoparticles [27]. More importantly, Isaacs et al. discovered that when the unsymmetrical guest ADA molecules
Olefin metathesis in multiblock copolymer synthesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 218–235, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.21
- , IBI, and SIBIS multiblock copolymers, which include glassy, rubbery, and semicrystalline polymer segments and demonstrate peculiar mechanical behavior [57][58]. References [59] and [60] report on the preparation of fluorescent polymer nanoparticles for bioimaging and in vivo targeting of tumors and
New amphiphilic glycopolymers by click functionalization of random copolymers – application to the colloidal stabilisation of polymer nanoparticles and their interaction with concanavalin A lectin
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2010, 6, No. 58, doi:10.3762/bjoc.6.58
- . Keywords: click chemistry; con A lectin; dynamic light scattering; glycopolymer; polymer nanoparticles; Introduction Over the last decades, research efforts in pharmaceutical, food and cosmetics technologies have been directed not only towards the syntheses of new bioactive entities or medicines, but also
- surfactants, are required to assure the colloidal stabilization of the polymer nanoparticles in aqueous medium. The properties of micelles (cmc, size and dynamics) depend on the chemical structures of amphiphilic copolymers. Macromolecular non-ionic surfactants appear to be the best suited from both the
- pyrrolidone) as the starting copolymer. Poly(NVP) is known to be biocompatible and to promote adhesion. NVP-based maleic copolymers have been reported for BSA immobilization [14] as well as for the preparation of polymer nanoparticles [10][15]. The choice of the carbohydrate moieties to be grafted onto the





































